-
Helpline
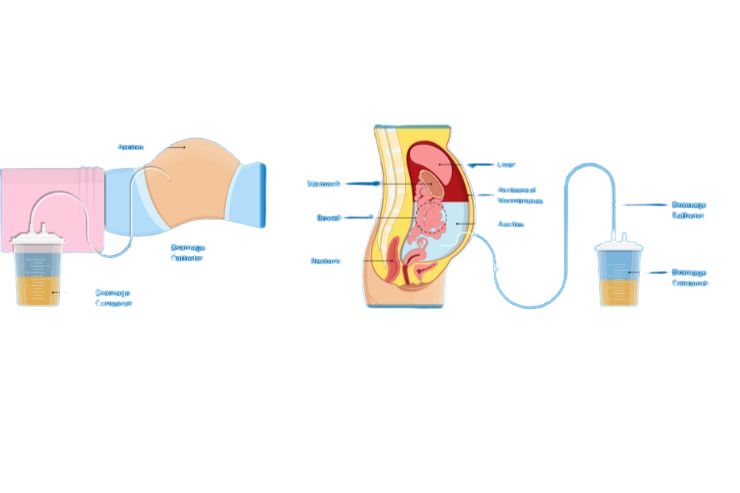
Paracentesis is a medical procedure used to remove excess fluid buildup from the abdominal cavity, a condition known as ascites. Ascites can occur due to various underlying conditions such as liver cirrhosis, heart failure, cancer, or infections. Paracentesis helps relieve symptoms associated with ascites, such as abdominal discomfort, difficulty breathing, and swelling.
Indications for Paracentesis
At Sandozi Health, paracentesis may be recommended for patients with the following conditions:
Procedure Overview
Before the paracentesis procedure:
During the paracentesis: